HARD SPOT INSPECTION TROLLEY - English -
Page 14/84
Operating and Maintenance Instructions
adaptaed from: https://app.box.com/s/c6qfgtuhfg1yd2ottrfum98x8jmg7rn3
| Hard spot inspection trolley • PLAMAT-M •
18201 |
|
| Operating and
Maintenance Instructions • V2.0 |
Fundamental principles
|
2 FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
2.1 Introduction
Steel manufacturing and steel
processing industries require nondestructive testing methods for
quality control. For this purpose hardness, case depth, strength and
residual stresses are major quality features in demand. Ferromagnetic
steels and cast iron show a distinct correlation between magnetic
behavior und mechanic technological materials characteristics.
Hard-magnetic materials, i.e., materials that are difficult to
magnetize or to degauss, mostly show mechanical hard and brittle
characteristics, while soft magnetic materials like pure iron use to be
mechanical ductile. Equally, residual and load stresses exert a
comparable influence on magnetic processes. Hence, in many cases these
nondestructively gauge-able magnetic properties can be used to analyze
mechanical material behavior and stress states.
The solution to address aforementioned
requirements is 3MA-X8. It is an acronym for “Micromagnetic
Multiparameter, Microstructure and stress Analysis“. Within fractions
of a second, the inspection system measure how hard- or soft-magnetic a
material is. Moreover, a multitude of different magnetic parameters are
determined which are correlated to different material properties or
residual and load stresses. By a pre-defined set of calibration samples
the 3MA method identifies the correlation between magnetically measured
parameters and the target values as required by the customer. This is
realized by mathematical statistical tools like pattern recognition and
regression analysis.
2.2 Measurement approach
3MA is a nondestructive electromagnetic
testing method, whereby testing statics were derived during magnetic
hysteresis cycles. 3MA evaluates electrical and magnetic parameters
which are influenced for example by the microstructure, hardness,
hardness depth, yield strength and residual stress states. Figure 1 is
pointing up the correlation between mechanical and magnetic material
properties. The mechanical properties of a material is resulting from
its microstructure, dislocations in the lattice and the mechanical
deformations by the production procedure. The micro magnetic properties
of a material are characterized by the dynamic magnetic behavior, which
is influenced by the interaction of Bloch walls (BW) with dislocations
or lattice defects.
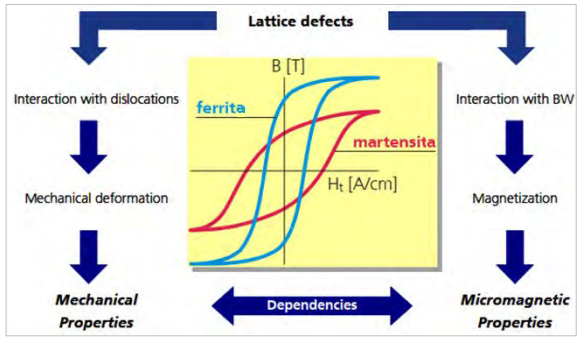
Figure 1: Correlation between mechanical and magnetic material properties
| ROSEN and IZfP Page 14 of
84 |
Confidential! |
|