PB_00 - Capítulo 5 - Análise de Fase - Página 5-035
traduzido do livro: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19780078298
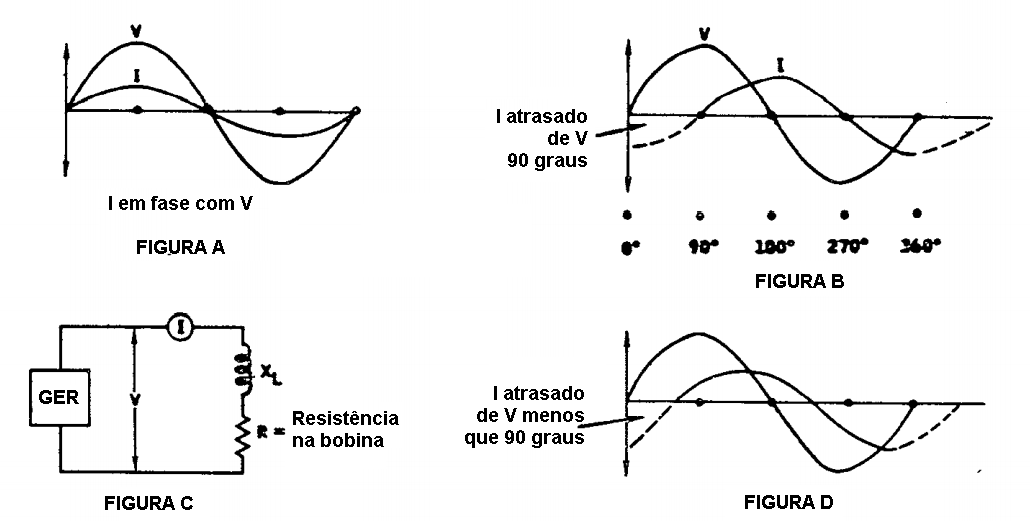
In some cases, the inductive reactance (XL) is so much greater than the
coil's resistance that we can disregard the resistance. Under these
conditions, it can be shown that the current (I) lags the voltage (V)
by 90 degrees as shown in view B. It can also be shown that when the
resistance is a significant value (views C and D) the current will lag
the voltage by a value less than 90 degrees. The current lag shown in
view D reresents the effect of both the coil's inductance reactance and
the resistance. A change in either value will change the lag between
the current and the voltage.
If a change
in the coil's magnetic field is made by the presence of a specimen,
will the lag between the current and the voltage:
......
Change.
...... Remain the same.
ÍNDICE
|